What do all those ratings on the glass mean?
NFRC Certified (upper left corner) indicates that the National Fenestration Ratings Council has licensed the window's manufacturer and certified the window's performance in accordance with NFRC's standards. The upper right corner identifies the window's manufacturer, model, style and the materials used in its construction.
The U-factor. The rate of heat loss from a building is indicated in terms of the U-factor (U-value). U-Factor ratings for windows generally fall between 0.20 and 1.20. The lower the U-value, the greater a window's resistance to heat flow and the better its insulating value. (The window's insulating value is indicated by the R-value, which is the inverse of the U-value.)
The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) indicates how well a product blocks heat from the sun. The SHGC is the fraction of incident solar radiation admitted through a window and absorbed and subsequently released inward. SHGC is expressed as a number between 0 and 1. Again, the lower the number, the better: A low SHGC means the window transmits less solar heat.
Visible transmittance is an optical property that indicates the amount of visible light transmitted. VT is expressed as a number between 0 and 1. The higher the VT, the more light is transmitted.
For more information on NFRC ratings, visit the organization's website at www.nfrc.org.
What Is a Low-e Window?
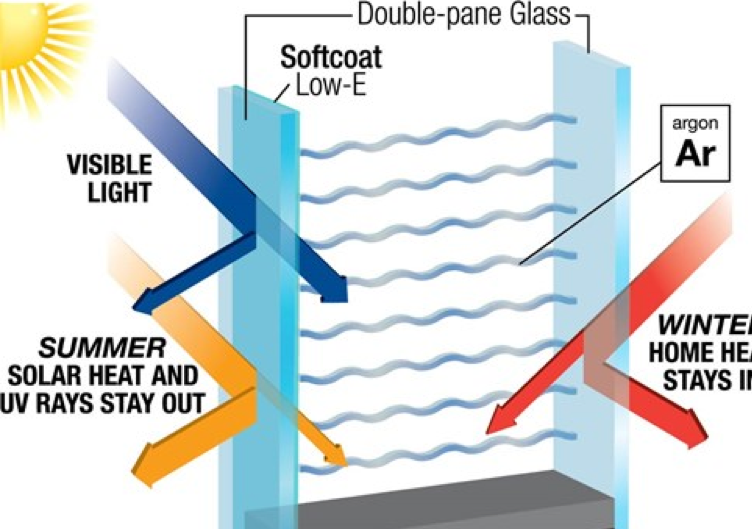
A low-e glass window (which stands for low emissivity) is simply a windowpane coated in microscopic layers of metallic oxides. The coating appears invisible to the naked eye, allowing as much natural light into the house as possible. However, though transparent, this coating also protects your home from unwanted UV rays which can burn your skin, fade your carpets, and damage your furniture. Plus, it also helps to control radiant heat (infrared light) as it enters and leaves a room. In other words, it keeps your house warmer in the winter by reflecting certain segments of the sun’s light spectrum back into the home, and cooler in the summer by reflecting particular sections outside. This saves on unnecessary utility expenses while creating a more comfortable living environment.
What Are Argon Gas-Filled Windows?
Argon gas windows feature a sealed unit, filled with gas between panes of glass to increase energy efficiency. Because argon gas is denser than air, adding it to the captive air in double-pane windows improves thermal insulation efficiency. Used in conjunction with a special low-E (short for low emissivity) glass coating, argon gas windows bring the temperature of the window closer to room temperature. This process ultimately eliminates air currents and drafts that occur when differing temperatures meet.
What causes condensation?
It’s natural to believe that your windows are the cause of condensation, but they aren’t. Windows don’t cause condensation; they simply prevent moisture from escaping to the outside and provide a highly visible surface on which to notice it. In fact, the “warm-edge” technology of high-performance replacement windows and doors can actually help reduce typical condensation buildup on glass. Nonetheless, while weather-tight, thermally efficient windows keep cold air outside, they also keep moisture in. Occasional, mild condensation is a normal event and causes no real problems. Even so, when you see excessive condensation on glass surfaces, take it as a warning that you may have excess humidity in your home.
How can I reduce humidity?
The best steps you can take for reducing excessive humidity levels and condensation in your home involve controlling sources of moisture and increasing ventilation:
- Use exhaust fans in your kitchen, laundry and bathrooms.
- Vent all gas burners, clothes dryers, etc. to the outdoors.
- Shut off furnace humidifiers and other humidifying devices in your home.
- Be sure that louvers in your attic or basement crawl spaces are open and amply sized.
- Open fireplace dampers to allow an escape route for moisture-laden air.
- Air out your house a few minutes every day.
What is tempered glass?
Tempered glass is defined as toughened glass that has been treated by heat or chemicals to increase its strength. Tempered glass has many benefits and uses which makes it a popular glass used in many home and commercial building projects. The most important benefit of tempered glass is safety. Tempered glass reduces the risk of injury due to its nature of breaking into small, circular pieces instead of sharp, jagged shards. Another benefit of tempered glass is its strength. Because the process of heating and applying chemicals strengthens the glass, tempered glass is an excellent choice for windshields, home windows and any other projects where maximum durability is desirable.
What is Impact Glass?
The most common way to achieve impact resistance in windows and doors is to select a product that uses laminated glass. Laminated glass is comprised of two panes of glass bonded together with a strong, clear interlayer. Laminated insulating glass is constructed as two panes of glass bonded together with a strong, clear interlayer, then includes an airspace followed by a third pane of glass for added insulation. The airspace between the 2nd and 3rd piece of glass is filled with air or other gas to reduce heat transfer.

